Train-hopping and zine-making: An interview with Railroad Semantics author Aaron Dactyl
Aaron Dactyl’s Railroad Semantics zines have flown off the shelves, racks, and rummage boxes since we started carrying them. They were so popular that we began to publish them as books. The fourth book just came out, and after a lot of work and design and effort, all four are now collected in a brand new box set, Railroad Semantics: Better Living Through Graffiti and Trainhopping.
 1. How did Railroad Semantics, the zine, start? How did they end up becoming books?
1. How did Railroad Semantics, the zine, start? How did they end up becoming books?
There were a lot of factors that played in to seriously making a zine. I guess the main thing is that I was doing all this really extensive traveling and had all these amazing pictures and stories and I wanted to make something out of them rather than just keep them to myself or within a small circle of friends. And I wasn’t really a writer at the time but I decided to learn. I came across an older train-hopping zine one day and sort of mimicked its layout, putting all the things together from my most recent trips. It took about two weeks to compile, and I started selling them at books shops in Portland. They sold fairly well and people seemed to like them so I made a second one, over the summer, at bit more ambitious than the first, and I eventually submitted that one to Microcosm and a couple other distributors. It was a big deal for me when Microcosm accepted the zine for distribution. Several years later, after I’d made several others, Microcosm contacted me about opting to publish each issue successively, and I went back through and re-edited them, which is a process that is still happening.

2. We did a signing together at a book fair last year, and it was cool to see the number of people who were excited about your books. Would you say you have a prototypical reader? Who do you end up connecting with about this stuff?
Ya, that was a first for me. It was interesting to see the wide array of people there. And as far as having a prototypical reader goes, other than just a general younger demographic, I hope not. It’s not that exclusive, I don’t think. I don’t play into the train-hopping or graffiti scenes at all and I’ve always wanted RR Semantics to be its own thing and to stand on its own. I consider it to be travel writing so I suppose if someone’s interested in the genre then it would appeal to them.
3. A lot of people see graffiti and think of it as either as expressive art or senseless vandalism. But it seems like there’s more to it than that, it’s quite political. Can you give a basic primer of what that is all about?

People’ve always had a love-hate relationship with graffiti. While it’s criminalized by society and prosecuted by the law, that same institution turns around and uses to promote the non-profit youth centers, political campaigns, and advertisements. Everyone wants to control it in their own way, and you can’t. Even on the inside, the people who do it turn into vigilantes and don’t want you to do it, or don’t like the way in which you do it. Graffiti’s an all inclusive sport (albeit, probably more of a bourgeois sport), and it goes back a long, long time—everybody knows this—to the Oregon Trail, Native American petroglyphs, and long before that. Only in the last hundred years or so did people start coming up with more creative monikers to express themselves, and pictures to go with, and in America, freight trains, because of their extensive range and high level of visibility, spawned a subculture that defies label. It’s not just hobo and train-hoppers that draw on train cars, it’s rail workers too, tramps in general, artists, punks, the whole gamut. And yet still certain people involved want to regulate that and for everyone to behave under a strict code of conduct because the rails are sacred and this and that. But that’s ridiculous, and egomaniacal.
4. What’s your next trip?
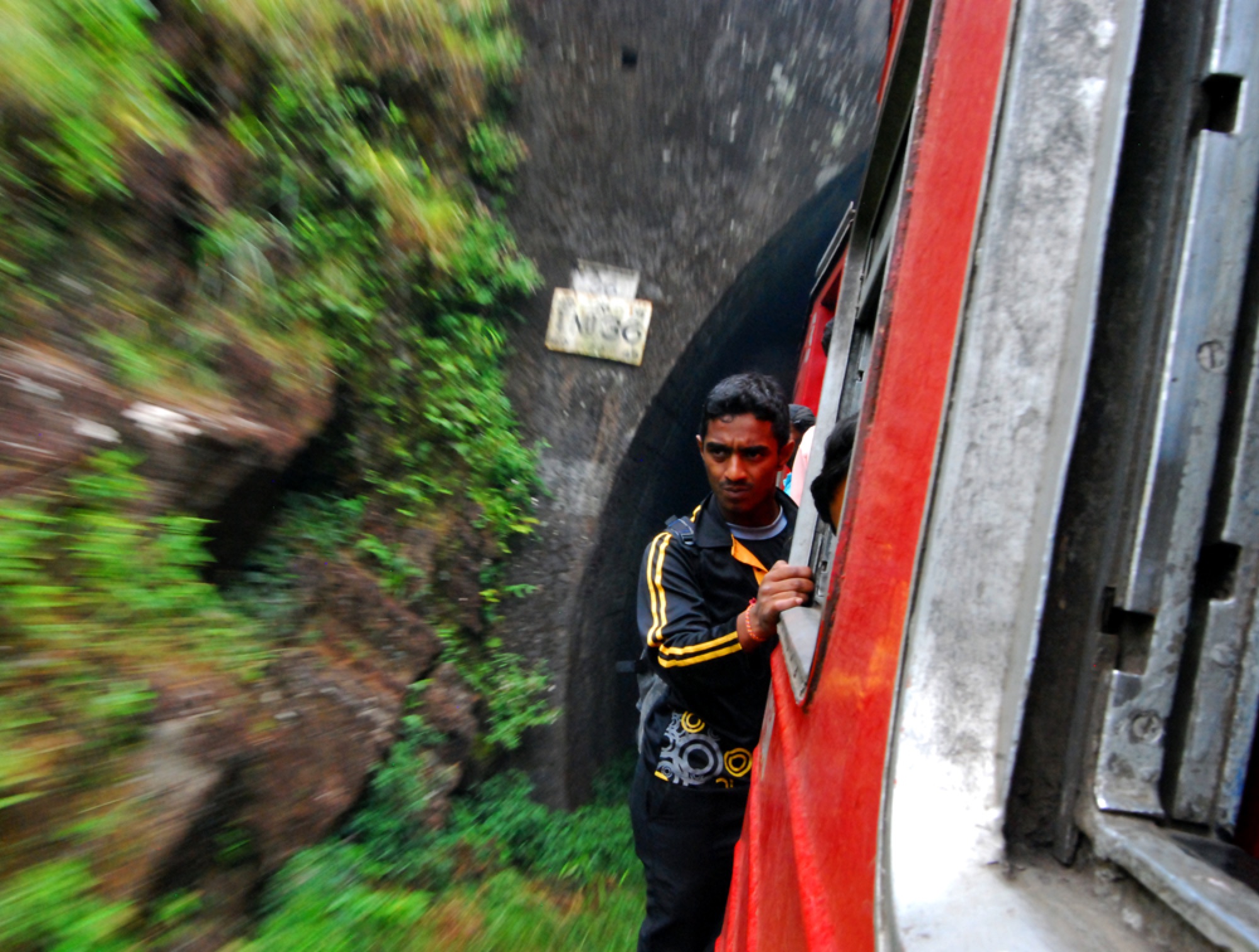

I’ve been able to do a lot of traveling over the last couple years outside the U.S., which was a first for me. Traveling in Southeast Asia for four months was a revelation, and a summer spent traveling across South America changed things for me completely. I have a couple of writing projects regarding those trips that I’m trying to get out of the way right now before I do any more serious traveling in the futures. But I may try and make it to Hawaii this summer. That’s a trip that’s been long overdue.
This has been an interview with Railroad Semantics author Aaron Dactyl. Our last author interview was with Velocipede Races author Emily June Street.
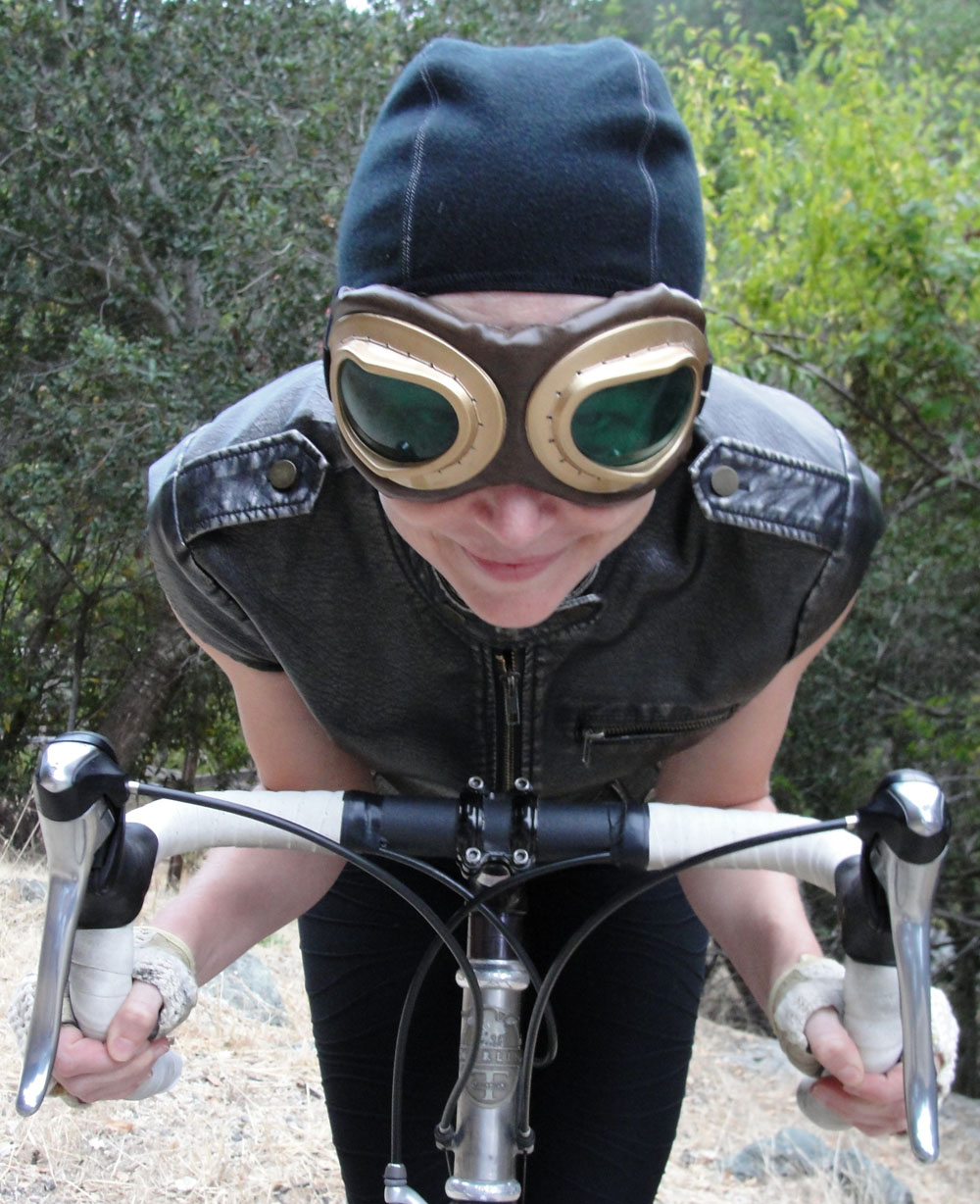 “A tough girl rebels against stifling gender rules in a quasi-historical steampunk world, dreaming of racing her bicycle in the cutthroat velocipede races. But can her dream survive scandal, scrutiny, and heartbreak?” That’s how
“A tough girl rebels against stifling gender rules in a quasi-historical steampunk world, dreaming of racing her bicycle in the cutthroat velocipede races. But can her dream survive scandal, scrutiny, and heartbreak?” That’s how 



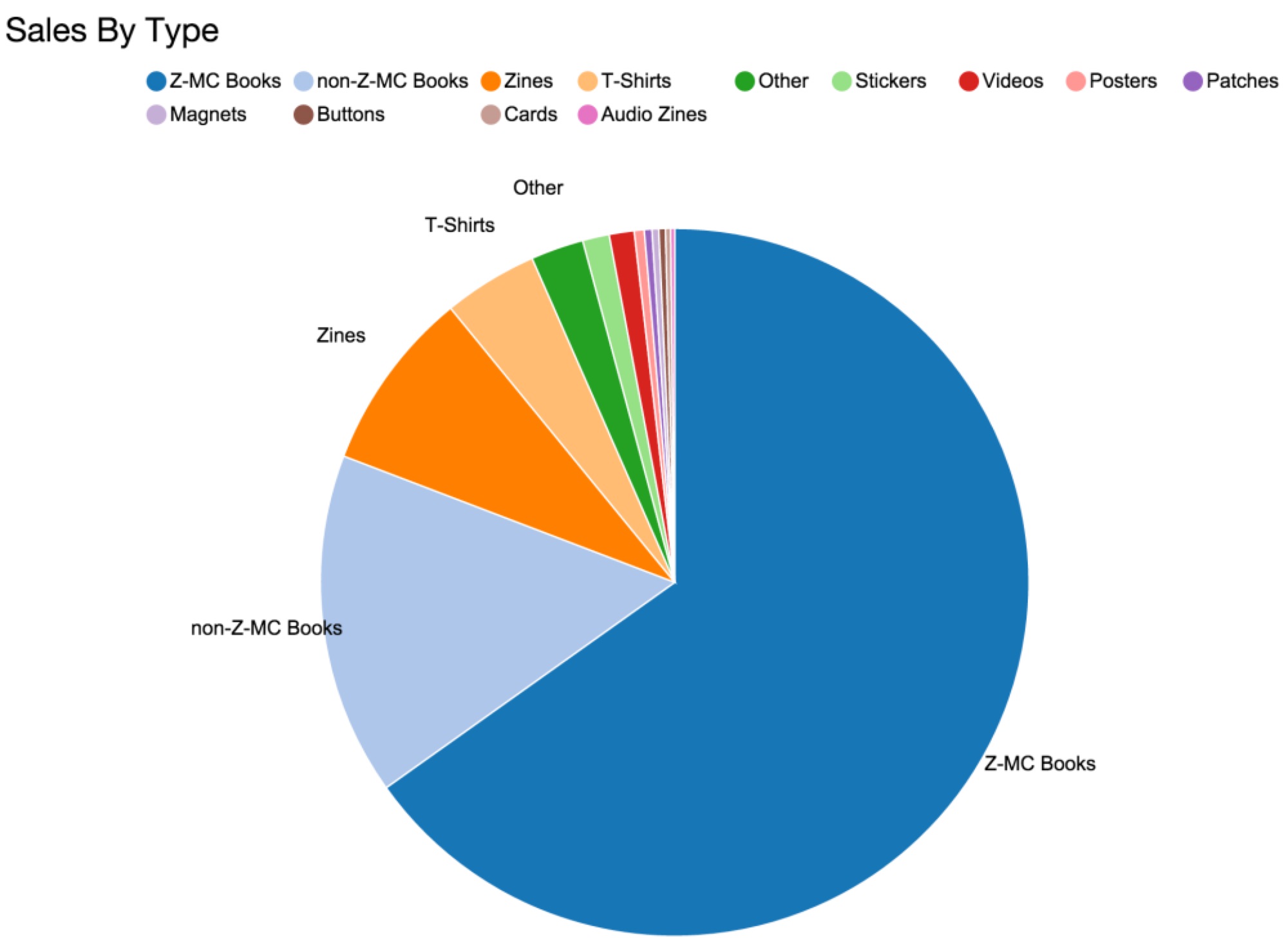
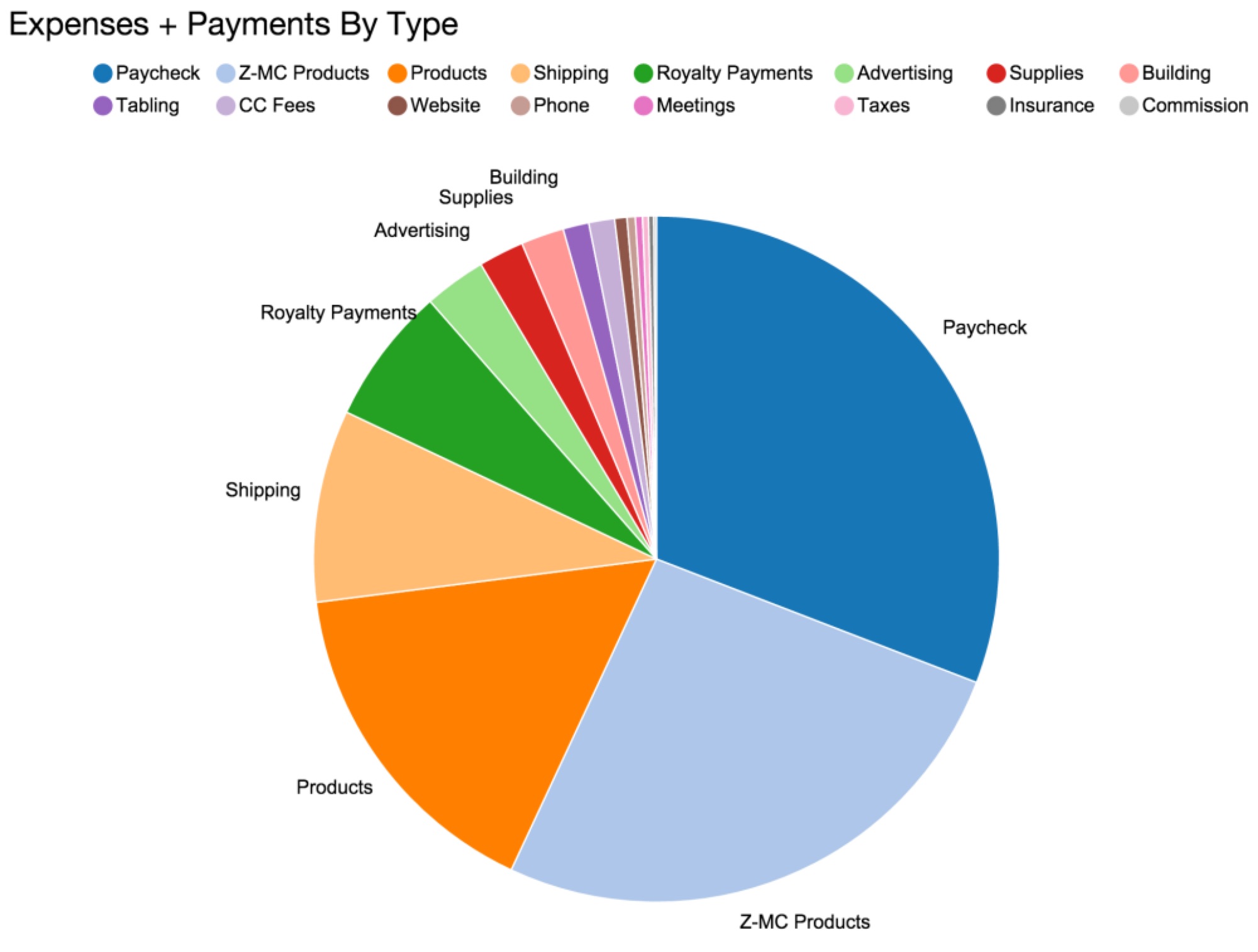
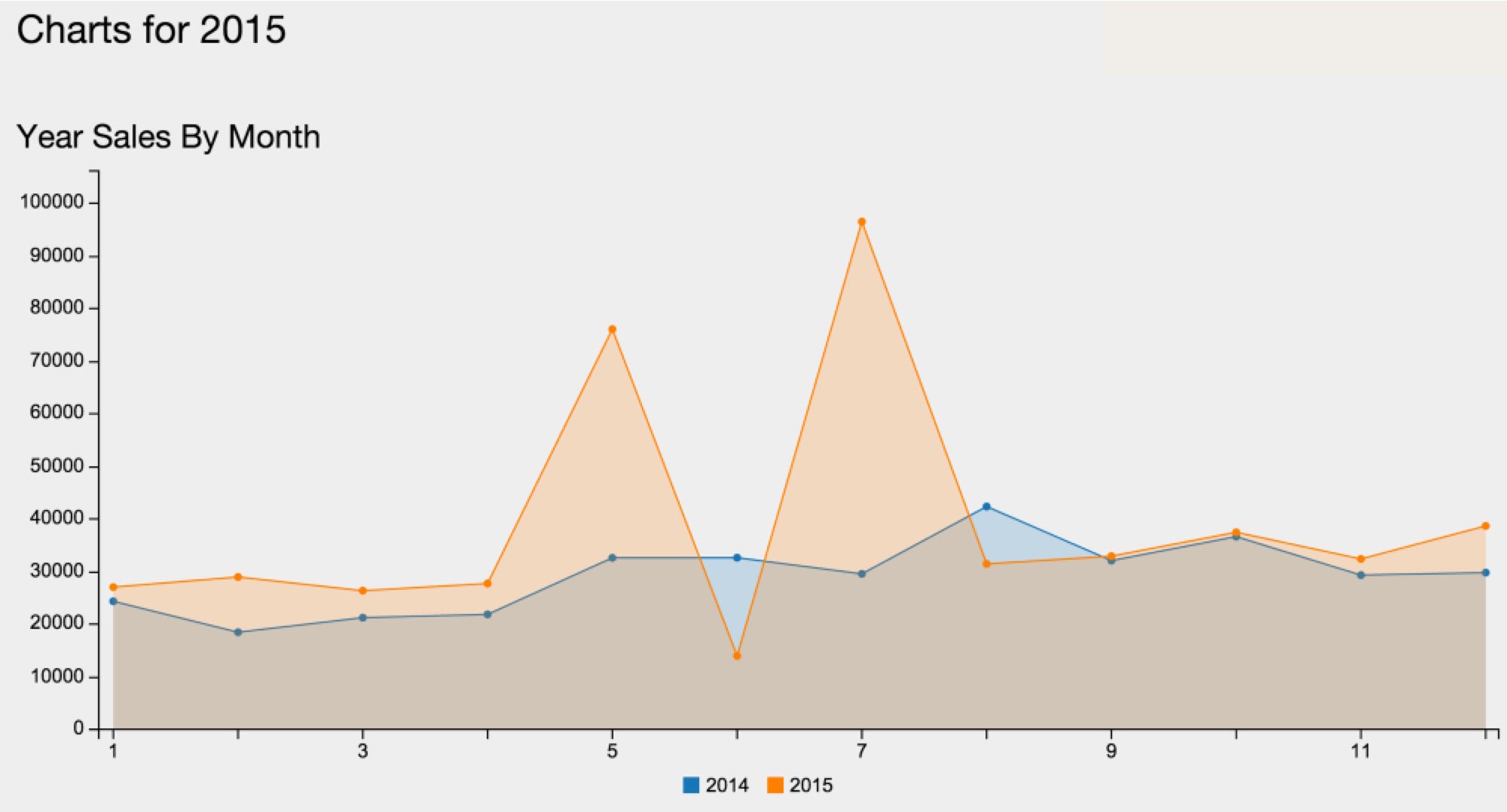
 Microcosm turns 20 this year! February 12, 2016 is our birthday. Not only are we almost old enough to drink, we’re really proud to have made it this far. There have been some rocky years back there, but things have been going well lately and it feels good to celebrate a milestone. So we’ll be celebrating properly: All year long.
Microcosm turns 20 this year! February 12, 2016 is our birthday. Not only are we almost old enough to drink, we’re really proud to have made it this far. There have been some rocky years back there, but things have been going well lately and it feels good to celebrate a milestone. So we’ll be celebrating properly: All year long.